New paper: Dry-roasted NUTS: early estimates of the regional impact of 2025 extreme weather
A new study has found that extreme weather events across Europe in the summer of 2025 caused significant economic losses, with impacts expected to intensify in the years ahead.
The paper, Dry-roasted NUTS: early estimates of the regional impact of 2025 extreme weather (Usman, Parker & Vallat, 2025), estimates that floods, droughts and heatwaves lowered gross value added (GVA) across affected European regions by €43 billion in 2025, equivalent to 0.26% of total EU output. Based on historical patterns, the researchers project that losses will deepen, reaching €126 billion by 2029.
Key findings:
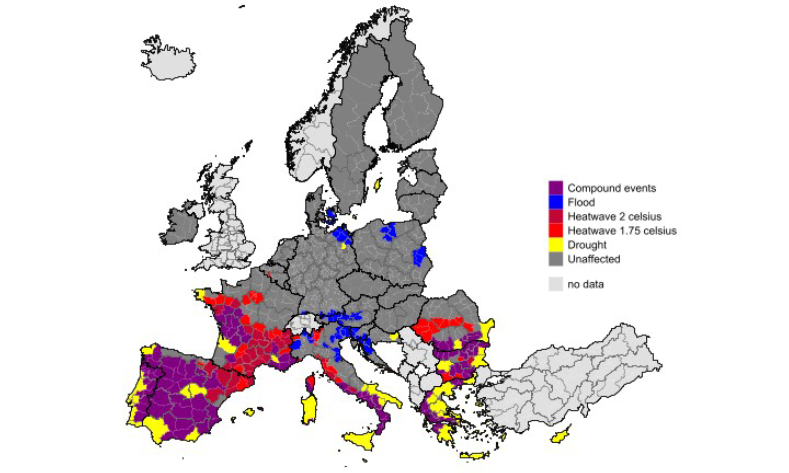
- Scale of impact: A quarter of EU NUTS3 regions were affected by extreme events in summer 2025.
- Heatwaves: 96 regions faced heatwaves, with French, Spanish, Italian & Bulgarian regions hardest hit. Aggregate EU heatwave-related losses were estimated at €6.8 billion in 2025, rising to €30 billion by 2029.
- Droughts: 195 regions suffered severe or extreme dryness, especially in Spain, Greece, Italy, Portugal and Bulgaria. EU-wide drought losses were estimated at €29.4 billion in 2025, increasing to €75.6 billion by 2029.
- Floods: 53 regions endured extreme wet conditions, notably in Italy and Slovenia. Flood-related losses reached €6.5 billion in 2025, projected to rise to €20.2 billion by 2029.
- Country impacts: Spain, Italy and France faced the highest combined losses. Spain alone recorded €12.2 billion in losses in 2025, projected to grow to €34.8 billion by 2029 (2.4% of its 2024 GVA).
- Future risks: The analysis excludes wildfire impacts — with one million hectares burned across the EU in 2025 — and compounding effects of simultaneous heatwaves and droughts. Actual losses are therefore likely higher than reported.
For full details, download and read the report at: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5484206
Citation: Usman, Sehrish and Parker, Miles and Vallat, Mathilde, Dry-roasted NUTS: early estimates of the regional impact of 2025 extreme weather (September 14, 2025). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5484206 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5484206